Step 6. Identify the facial nerve
6.1 Identify the bone over the lateral semicircular canal.
6.2 Remove cellular bone from the deep aspect of the ear canal and the gutter between the sigmoid sinus and facial nerve.
6.3 Safe dissection of the facial nerve uses the incus and lateral semicircular canal landmarks above and the digastric ridge below. These in turn require that the position of the middle fossa, sigmoid sinus and outer ear canal are demonstrated. Make a point of carefully removing the cells against the canal wall that form a slope from the digastric ridge to the incus.
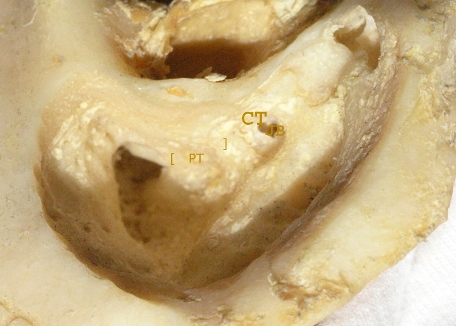 6.4 In a well pneumatised temporal bone there are two more features that indicate the position of the facial nerve. The sentinel cell marks the start of the posterior tympanotomy through which fluid may be aspirated from the middle ear. 6.4 In a well pneumatised temporal bone there are two more features that indicate the position of the facial nerve. The sentinel cell marks the start of the posterior tympanotomy through which fluid may be aspirated from the middle ear.
6.5 A series of cells pass medial to the facial nerve toward the jugular bulb.
|
